Perfect Competition | A-Level Economics Notes
These revision notes cover everything you need to know about Perfect Competition for A-Level Economics. They're designed for students studying AQA A-Level Economics, Edexcel A-Level Economics, and Edexcel International A-Level Economics. Written by Jaisul Naik, UCL Economics graduate and A-Level Economics tutor since 2017.
What are the characteristics of perfect competition?
- no barriers to entry or exit
- perfect information
- identical products
- firms are price-takers
Perfect competition diagram in the short-run
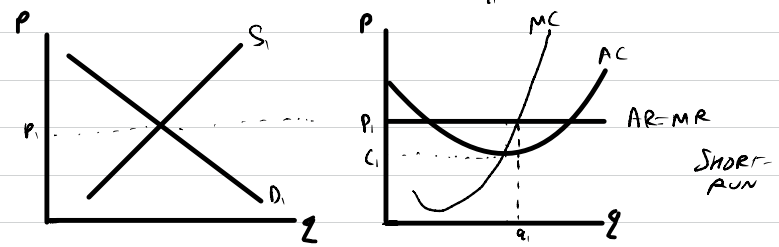
Efficiencies in the short-run
- not productively efficient because MC≠AC at q1
- allocatively efficient because AR=MC at q1
What happens in the long-run in perfectly competitive markets?
- existing firms are making supernormal profit.
- since there is perfect information and no barriers to entry,
- new firms are attracted to join the market
- market supply increases
- each firm has less demand so AR and MR shifts to the left
- existing firms attempt to profit maximise but now they are only able to make normal profits
Perfect competition diagram in the long-run
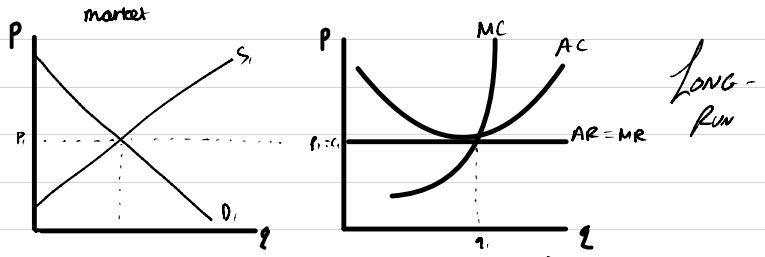
Efficiencies in the long-run
- productively efficient because MC=AC at q1
- allocatively efficient because AR=MC at q1
- not dynamically efficient because firms are not making supernormal profit in the long-run
Summary questions
- what are the characteristics of perfect competition?
- perfect competition short-run diagram
- is perfect competition efficient in the short-run
- what happens in perfect competition in the long-run?
- perfect competition long-run diagram
- is perfect competition efficient in the long-run
A-Level Economics Tutoring
I offer one-to-one and small group A-Level Economics tutoring for students across the UK and internationally. With 87+ five-star Google reviews and tutoring experience since 2017, I specialise in helping students understand difficult concepts and improve their exam technique.