Indirect Taxes | A-Level Economics Notes
These revision notes cover everything you need to know about Indirect Taxes for A-Level Economics. They're designed for students studying AQA A-Level Economics, Edexcel A-Level Economics, and Edexcel International A-Level Economics. Written by Jaisul Naik, UCL Economics graduate and A-Level Economics tutor since 2017.
What is an indirect tax?
An indirect tax is an extra cost imposed by the government on firms.
How does an indirect tax affect equilibrium price and quantity?
An indirect causes market supply to decrease. This causes a contraction in demand. This causes price to increase from p1 to p2 and quantity to fall from q1 to q2.
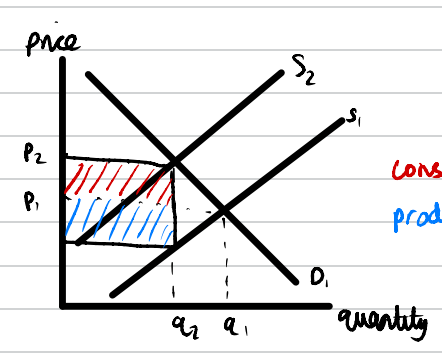
What is the impact of an indirect tax on consumers, producers and the government?
producers
- the blue shaded rectangle shows the producer burden of the tax.
- as a tax is an extra cost of production, this reduces firms' profits.
consumers
- the red shaded rectangle shows the consumer burden of the tax.
- consumer surplus decreases as they have to pay a higher price for the good/service.
- indirect taxes are regressive, which means they impact low income households more than high income households
government
- the shaded rectangle shows the tax revenue collected by the government.
- this is useful as it can fund government spending on a targeted area such as the NHS
- this is particularly useful as demerit goods like vapes cause a burden on the NHS.
- as smokers end up paying towards the NHS' costs, the externality is now internalised.
deadweight loss
- the entire rectangle includes producer burden and consumer burden but this is not entirely lost as the government gain tax revenue by the exact same amount
- therefore, the triangle shows the amount of deadweight loss
- this is the consumer and producer surplus that has been entirely lost from the market.
- this is an example of a market distortion which is a common source of goverment failure.
- it is important that the deadweight loss is worth it in terms of the size and damange of the initial market failure.
What is the impact of price elasticity of demand on indirect taxes?
- An indirect tax has different effects on a market if the good or service is price inelastic in demand.
- Demand is inelastic if percentage change in demand is small in relation to the price change caused by the indirect tax.
- Demerit goods may be inelastic if they are addictive but also if they cost a small proportion of total income.
- The effects can be seen on the diagram below.
- It shows that while price increases from p1 to p2, quantity only falls a small amount from q1 to q2.
- This is an example of government failure in the form of unintended consequences and imperfect information. If the government did not foresee how addictive cigarettes are, the intervention would fail to reduce consumption to the socially optimal target.
- Furthermore, firms know that they can raise prices and increase their total revenue when a good is inelastic.
- This causes consumer burden to increase significantly.
- The one benefit in this case is that it is now quite easy for the government to collect more tax revenue. This could be used in other forms of government intervention such as provision of information.
What are the possible sources of government failure with indirect taxes?
- market distortions - deadweight loss
- imperfect information - the size of the externality, PED.
- unintended consequences - if demand is inelastic, black markets
Summary questions
- What is an indirect tax?
- How does an indirect tax affect a market?
- What is the burden of an indirect tax on consumers, producers and the government?
- What is the impact of price elasticity of demand on indirect taxes?
- What are the possible sources of government failure with indirect taxes?
A-Level Economics Tutoring
I offer one-to-one and small group A-Level Economics tutoring for students across the UK and internationally. With 87+ five-star Google reviews and tutoring experience since 2017, I specialise in helping students understand difficult concepts and improve their exam technique.