Fiscal Policy | Notes
These revision notes cover everything you need to know about Fiscal Policy for A-Level Economics. They're designed for students studying AQA A-Level Economics, Edexcel A-Level Economics, and Edexcel International A-Level Economics. Written by Jaisul Naik, UCL Economics graduate and A-Level Economics tutor since 2017.
What is fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending or taxation in order to influence aggregate demand.
What is expansionary fiscal policy?
Expansionary fiscal policy is when the government increase spending or decrease taxes, causing aggregate demand to shift to the right.
What is contractionary fiscal policy?
Expansionary fiscal policy is when the government decrease spending or increase taxes, causing aggregate demand to shift to the left.
What is a balanced budget?
A balanced budget is when government spending = tax revenue
What is a budget deficit?
A budget deficit is when government spending is more than tax revenue
What is a budget surplus?
A budget deficit is when government spending is less than tax revenue
What is national debt?
National debt is an accumulation of the budget deficit each year.
What is the impact of expansionary fiscal policy on macroeconomic performance?
- expansionary fiscal policy could involve a increase in spending or a decrease in taxes
- for example, the government could decrease income taxes
- this means that disposable incomes would increase
- this means that consumer spending would increase
- AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
- this would cause aggregate demand would shift to the right
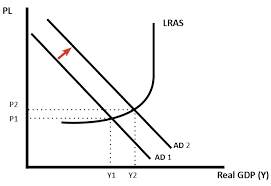
- the diagram shows that real gdp increases from y1 to y2 (economic growth)
- this also causes unemployment to decreases.
- because demand for labour is derived from the demand for goods and services.
- furthermore, there is an increase in the price level (demand-pull inflation) from p1 to p2
- this is because there is more demand chasing the same amount of goods and services
What is the impact of expansionary fiscal policy on the budget?
- expansionary fiscal policy would lead to an increase in the budget deficit
- this means that national debt would increase
- national debt is the accumulation of budget deficits over time
- national debt means high interest payments in the future, which takes up room in the budget
- furthermore, future generations will see austerity measures to repay the debt
- this can in the form of higher taxes or spending cuts
- this can lead to a decline in living standards
What is the crowding out effect?
- expansionary fiscal policy involves an increase in government spending or a decrease in taxes
- in order to fund this, the government could borrow money by selling more bonds to the private sector
- this reduces the spending power of individuals or firms in the private sector
- therefore, any increase in government spending could be crowded out by a decrease in consumer spending or business spending
- this means that aggregate demand might not increase as much as it was intended for
- however, the people buying government bonds may have a higher income therefore a lower marginal propensity to consume
- the government could target spending or tax cuts to low income households
- since their marginal propensity to consume is higher, this leads to a higher multiplier effect as k=1/(1-MPC)
What is the impact of contractionary fiscal policy on macroeconomic performance?
- contractionary fiscal policy is when the government increases taxes or decreases spending.
- for example, the government might increase income taxes.
- this means that consumers have less disposable income
- this means that consumer spending would fall
- AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
- this means that aggregate demand would shift to the left
- there is less demand for the same number of goods and services
- this causes the inflation rate to fall from p1 to p2.
What is the impact of contractionary fiscal policy on the supply-side?
- contractionary fiscal policy involves a decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes
- this could weaken the supply side of the economy
- for example, the government could increase income taxes to reduce the budget deficit or aggregate demand.
- however, this also reduces the incentive for people to work.
- this means that there would be a decrease in people who are willing and able to work
- for example, people may take earlier retirement than usual or skilled workers might migrate to another country
- this has two downsides
- firstly, it is going to worsen the budget deficit because the governent would collect less tax as a result of people leaving the workforce
- secondly, long-run aggregate supply would shift to the left
- as the productive capacity of the economy falls.
- this would cause further inflation
What does the Laffer curve show?
- As tax rates increase, tax revenue also increases up to a point.
- After this point, further increases in tax rates cause people to leave the workforce.
- People may choose to migrate away from the country or take early retirement or work less hours.
- This causes tax revenues to fall.
What is the impact of contractionary fiscal policy on inequality?
Summary questions
- what is fiscal policy?
- what is expansionary fiscal policy?
- what is contractionary fiscal policy?
- what is a balanced budget?
- what is a budget deficit?
- what is a budget surplus?
- what is national debt?
- impact of contractionary fiscal policy on macroeconomic performance
- what is the impact of expansionary fiscal policy on the budget?
- what is the crowding out effect?
- impact of contractionary fiscal policy on macroeconomic performance
- what is the impact of contractionary fiscal policy on the supply-side?
- what does the Laffer curve show?
- what is the impact of contractionary fiscal policy on inequality?
A-Level Economics Tutoring
I offer one-to-one and small group A-Level Economics tutoring for students across the UK and internationally. With 87+ five-star Google reviews and tutoring experience since 2017, I specialise in helping students understand difficult concepts and improve their exam technique.