Comparative Advantage | A-Level Economics Notes
These revision notes cover everything you need to know about Comparative Advantage for A-Level Economics. They're designed for students studying AQA A-Level Economics, Edexcel A-Level Economics, and Edexcel International A-Level Economics. Written by Jaisul Naik, UCL Economics graduate and A-Level Economics tutor since 2017.
What is absolute advantage?
Absolute advantage is when a country is able to produce a good or service at a lower cost.
What is comparative advantage?
Comparative advantage is when a country is able to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost.
How do you calculate opportunity cost?
Make a ratio for good A : good B.
Simplify the ratio in the form 1 to n.
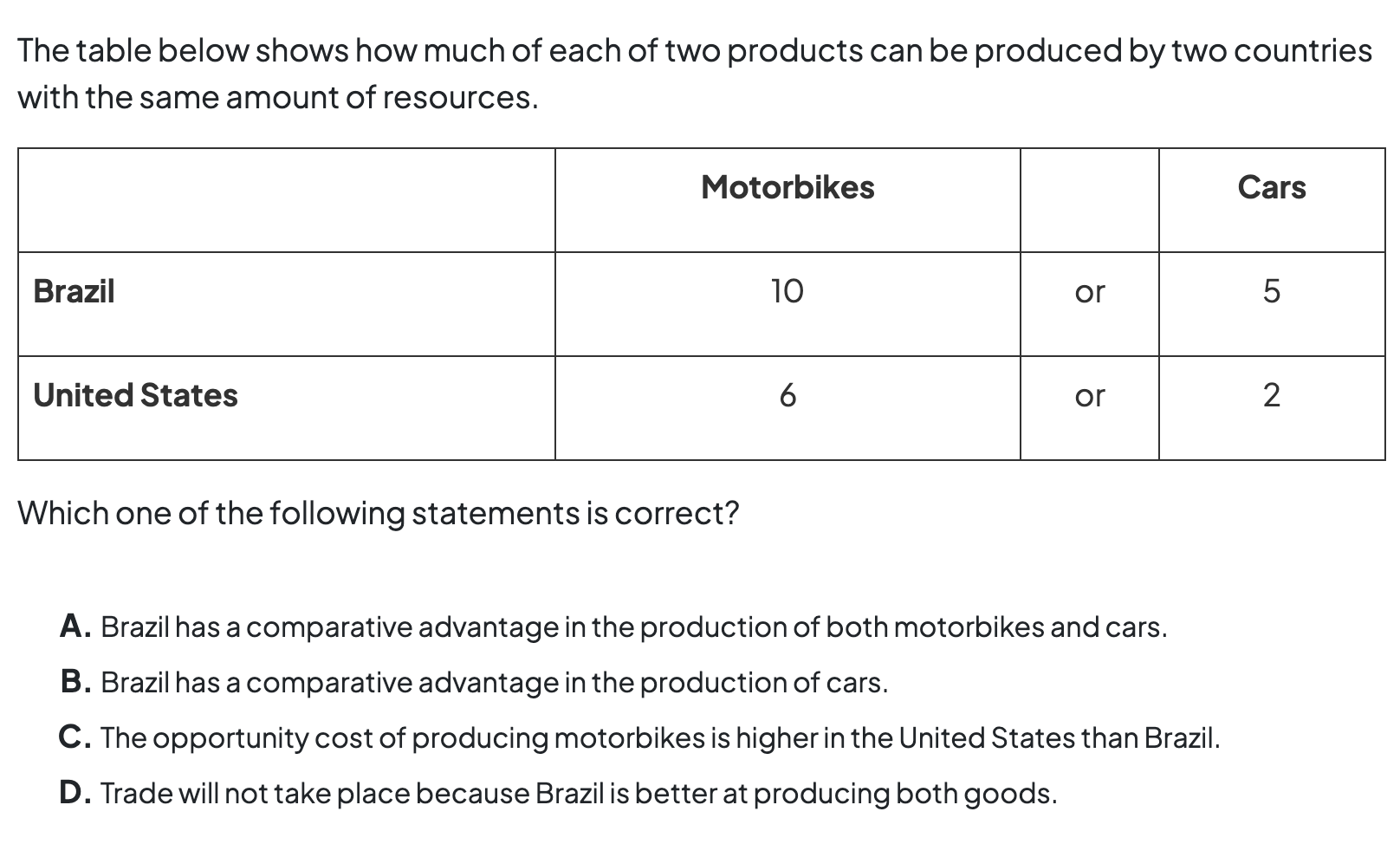
Practice question 1
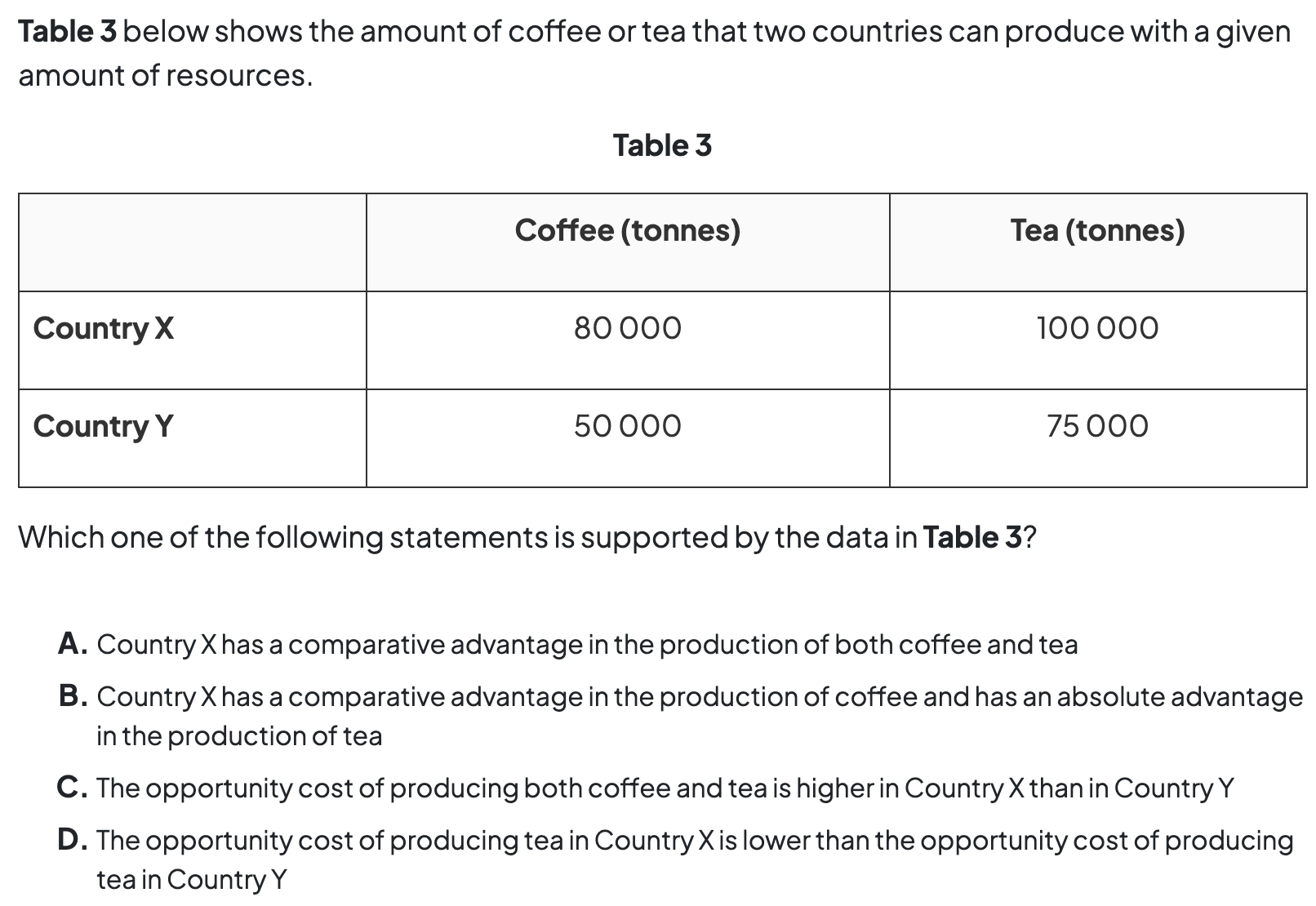
Practice question 2
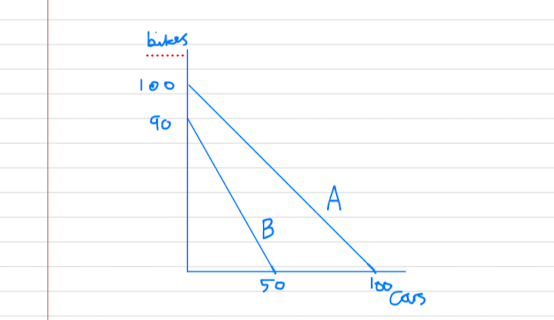
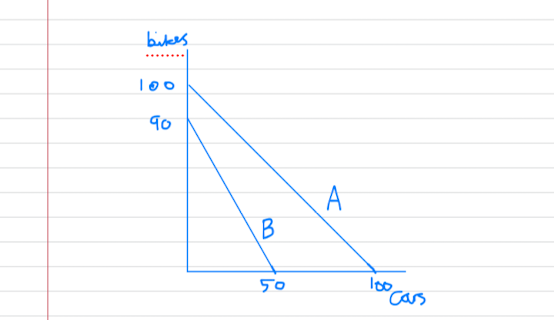
Advantages of specialisation and free trade
- due to globalisation, countries are encouraged to specialise in the goods and services where they have a comparative advantage.
- countries will have a comparative advantage in the goods or services with the lowest opportunity cost to produce.
- comparative advantage theory suggests that specialisation should lead to an increase in total output.
- the diagram shows an example of country A and country B who are able to produce cars and bikes.
- if each country produced at the half way point on their PPF, then country A would be able to make 50 bikes and 50 cars whilst country B would be able to make 45 bikes and 25 cars. The total world output would be 170 units.
- however, if country A specialised fully in cars and country B specialised fully in bikes then the total world output would be 190.
- then, each country would be open to trade.
- if each country is capable of producing more output with its available factors of production, this can be illustrated with an increase in productive potential, and a right shift in LRAS.
- overall specialisation would lead to an increase in total output.
What are some disadvantages or assumptions of comparative advantage theory?
- transport costs may outweigh comparative advantage gains
- model assumes constant returns to scale
- increased specialisation may lead to diseconomies of scale
- leads to over-dependence and vulnerability to external shocks
- governments may impose protectionism
Summary questions
- what is absolute advantage?
- what is comparative advantage?
- how do you calculate comparative advantage?
- practice question 1
- practice question 2
- what are the advantages of specialisation and trade?
- what are the disadvantages or assumptions of comparative advantage theory?
A-Level Economics Tutoring
I offer one-to-one and small group A-Level Economics tutoring for students across the UK and internationally. With 87+ five-star Google reviews and tutoring experience since 2017, I specialise in helping students understand difficult concepts and improve their exam technique.